Control flow using "if"
Execution Flow
- Code Executed line-by-line
- Actions are performed & control flow may change
- Specific conditions can change control flow
- "if"
- "else"
- Specific conditions can change control flow
Example - Simple Flow
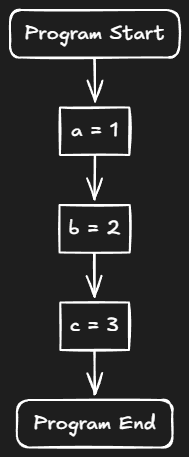
let a = 1;
let b = 2;
let c = 3;
Example - if..else
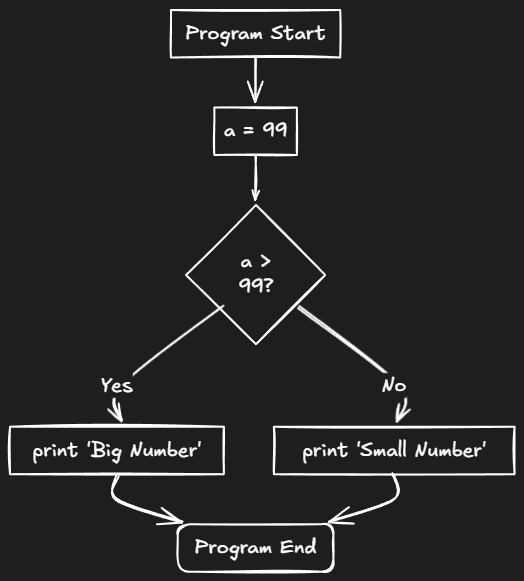
let a = 99;
if a > 99 {
println!("Big number");
} else {
println!("Small number");
}
Example - Nested if..else
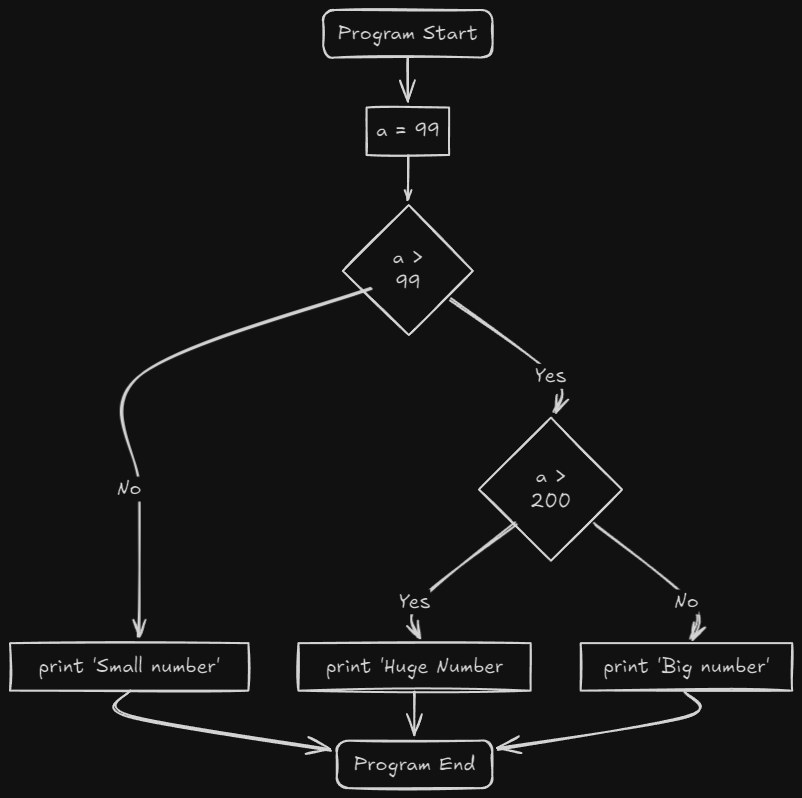
let a = 99;
if a > 99 {
if a > 200 {
println!("Huge number");
} else {
println!("Big number");
}
} else {
println!("Small number");
}
Example - if..else if..else
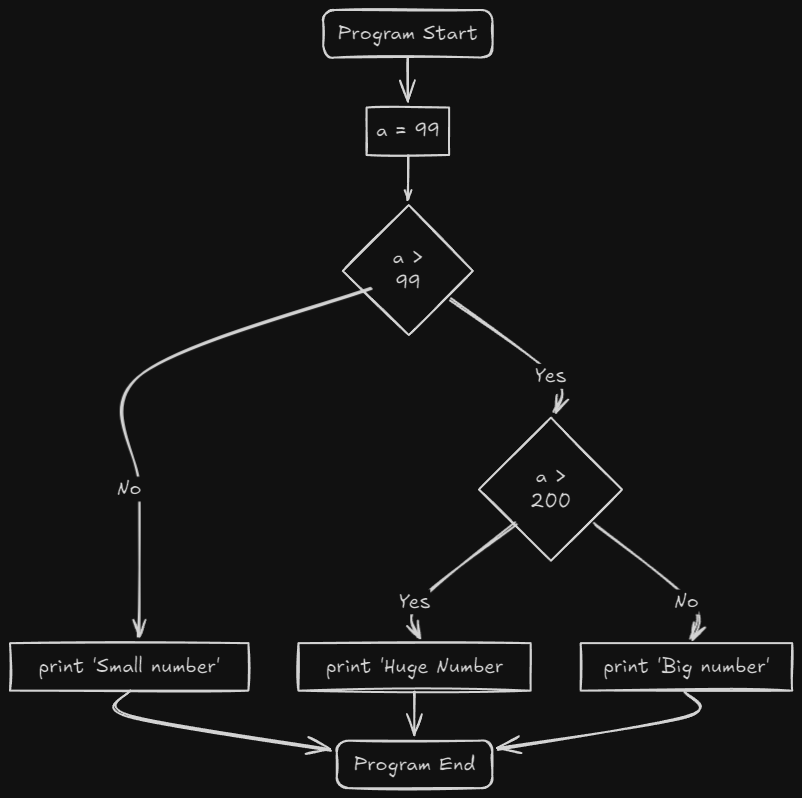
let a 99;
if a > 200 {
println!("Huge number");
} else if a > 99 {
println!("Big number");
} else {
println!("Small number");
}
Note
Same thing just instead of nesting using else if (which is checked only when the if and else if above it evaluate to false)
let a 99;
if a > 99 {
println!("Big number");
} else if a > 200 {
println!("Huge number");
} else {
println!("Small number");
}
This will not work
Because the first if if a > 99 is checked first, when we have a number bigger than 200 it will evaluate o true because said number is bigger than 99 and so the checks will never reach the 200 part